A 503 Service Unavailable Error is an HTTP response status code indicating that a server is temporarily unable to handle the request. This may be due to an overloaded server or a server that's down for maintenance. This particular response code differs from the 500 Internal Server Error we explored some time ago. While a 500 Internal Server Error indicates an issue preventing the server from handling the request entirely, a 503 Service Unavailable Error indicates that the server is still functioning properly and can process the request, but has opted to return the 503 response code.
There are dozens of possible HTTP status codes used to represent the complex relationship between the client, a web application, a web server, and multiple third-party web services. As you can imagine, determining the cause of a particular status code can be challenging. That's why, in this article, we'll examine the 503 Service Unavailable Error in-depth. By the end of this article, you'll know what a 503 Service Unavailable Error is and how to troubleshoot and fix it.
The Problem is Server-Side
All HTTP response status codes that are in the 5xx category are server error responses. Unlike the 502 Bad Gateway Error, which indicates that a server somewhere in the connection chain is down or unavailable; a 503 Service Unavailable Error indicates that the server is temporarily unable to handle the request but is otherwise functioning as normal. Furthermore, unlike gateway-related 5xx response codes that indicate issues either on the web server or another server further upstream, the 503 Error code indicates an issue on the actual web server hosting your application.
In most cases, the web server should provide a user-friendly page showing that the service is temporarily unavailable. Additionally, the application should send a Response-After HTTP header. This header should inform the user agent (client) how long it should wait to attempt the request again. This value should either be a Date value indicating the timestamp the service will be available, or a numeric value indicating how many seconds from now the user agent must wait to retry.
Since a 503 Error means something is wrong with the server of your application, you can disregard the client side of things. That means you can ignore most client-side code and components, such as HTML, cascading style sheets (CSS), client-side JavaScript, etc.
This doesn't apply solely to websites, either. Normal web applications will often power smartphone apps that have a modern-looking user interface. If a 503 Service Unavailable Error occurs on a smartphone app, the issue will lie outside of the installed app. The problem will be something on the server-side, which performs most of the logic and processing for the app.
That's the 503 Service Unavailable Error in a nutshell. In the next section, we'll go over how to diagnose and fix this error.
Start With a Thorough Application Backup
Before attempting any fixes or changes to the system, perform a full backup of your application, database, and so forth. Otherwise, you might find yourself with additional errors and latent errors. If you have the capability, create a complete copy of the application onto a secondary staging server that isn't "live." This will give you a clean testing ground to test all potential fixes to resolve the issue without threatening the security or sanctity of your live application.
Diagnosing a 503 Service Unavailable Error
As mentioned before, a 503 Error indicates that the server (typically the actual web server on which your application is running) is temporarily unavailable. This is usually due to the server being "down" for scheduled maintenance or due to a heavy traffic load that prevents it from properly serving all incoming requests.
The Server is Down for Maintenance
A 503 Error should pop up if the server is down for maintenance. The server has not actually crashed or shut down but is in a mode of service that prevents requests from behaving as normal. That is why a once normally-functional page will display a 503 Service Unavailable Error, alongside a message about the server being down for maintenance. Only administrators will have access to the server, whereas normal public requests will be turned away until maintenance is complete.
The Server is Overloaded
A server will reject requests due to overload from an unexpected onslaught of traffic and incoming requests. Basically, the server has throttled itself in order to maintain some semblance of normal behavior for a portion of requests. If the application/server is configured correctly, you should be able to complete the request by waiting and retrying a few times. By waiting, the traffic spike should die down and let you in.
If the error is not the result of maintenance or overload, then you'll need to troubleshoot further.
We'll go over some troubleshooting tips and tricks to help you resolve this issue. If nothing here works, don't forget that Google is your friend. Search for specific terms related to your issues. Chances are you'll find others who have experienced this issue and found ways to resolve it.
Troubleshooting on the Server-Side
Most of the time, a 503 Service Unavailable Error results from maintenance or a traffic overload. When that's not the case, here are some additional tips to help you troubleshoot what might be causing this error.
Reboot the Server
There could be a bottleneck within your app's server chain causing a 503 Error. One of the simplest solutions to this is to restart the web server hosting the application. If your application is spread over multiple servers, make sure all are rebooted properly to bring the system back online as normal.
Check for Unexpected Maintenance
Your server and/or application may be automatically configured to go down for maintenance. Many modern content management systems, like WordPress, will automatically download and install updates to their base software without any intervention on your behalf. The web server could be issuing a 503 Service Unavailable Error during this period. If you're able to access the administration settings of your application/server, check the configuration options for automatic maintenance scheduling. You may have the option to disable this setting if you'd rather have direct control over that process. Don't forget to upgrade to newer versions fairly regularly, as they typically include critical security fixes.
Server Connectivity Issues
A 503 Error may indicate that a server somewhere in the chain is down or unreachable. Most modern applications don't reside on a single server. Instead, applications are spread over multiple systems or rely on third-party services to function. If one of these servers goes down, you might see a 503 Error that appears to be from your own application.
Improper Firewall Configuration
A firewall is a basic security device that monitors network traffic and acts as a gatekeeper. It helps decide which traffic is safe and which could be malicious. In most cases, firewalls stop potentially harmful traffic (and may be logged for network admin use). But it's possible that a firewall configured somewhere on the network is preventing critical traffic from getting through. This is particularly true for applications that rely on content delivery networks (CDNs). These CDNs act as a third-party host for "heavy" content like images or videos on behalf of your application, so your application can maintain its speed and efficiency. However, automatic firewall services sometimes perform false positives, mistaking perfectly safe and valid content from CDNs as malicious. When this happens, the firewall will shut off that stream of content, leading to a 503 Error.
Check the Logs
Nearly every web application will keep some form of server-side logs, such as Application Logs and Server Logs.
-
Application logs:These logs contain the history of what the application did. This usually includes requested pages, connected servers, database results, and so forth.Server logs: These logs are related to the actual hardware running the application and will often provide details about the health and status of all connected services, or just the server itself. Google "logs [PLATFORM_NAME]" if you're using a CMS, or "logs [PROGRAMMING_LANGUAGE]" and "logs [OPERATING_SYSTEM]" if you're running a custom application to get more information on finding the logs in question.
Application Code or Script Bugs
If all else fails, check your code. A bug could be causing the 503 Service Unavailable Error. Try diagnosing the issue by manually debugging your application and parsing through application and server logs. Ideally, make a copy of the entire application to a local development machine and perform a step-by-step debug process. This will allow you to recreate the exact scenario in which the 503 Service Unavailable Error occurred. Once you know why the error occurred, you can go about fixing it.
A 503 Service Unavailable Error within your web application is a strong indication that you may need an error management tool. That's where Airbrake comes in. Airbrake Error & Performance Monitoring software provides real-time error monitoring and automatic exception reporting for all your development projects. Airbrake's dashboards ensure you receive round-the-clock status updates on your application's health and error rates.
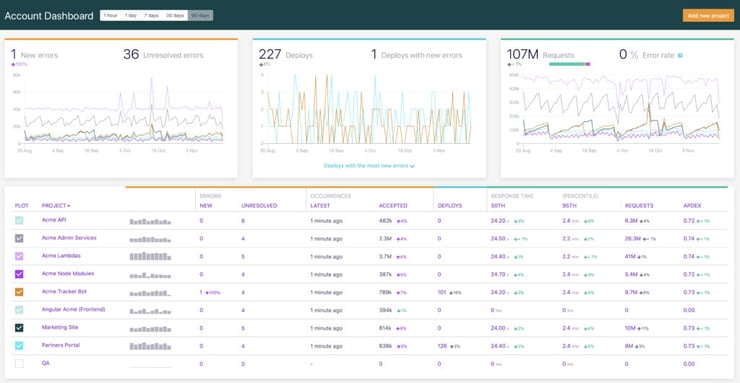
Plus, Airbrake makes it easy to customize exception parameters while giving you complete control of the active error filter system, so you only gather the errors that matter most.
Check out Airbrake's error monitoring software today and see for yourself why so many of the world's best engineering teams use Airbrake to revolutionize their exception handling practices!
Note: We published this post in November 2017 and recently updated it in January 2022.